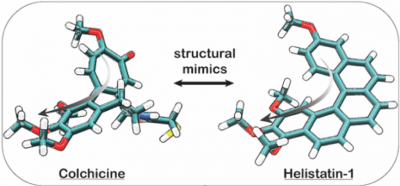
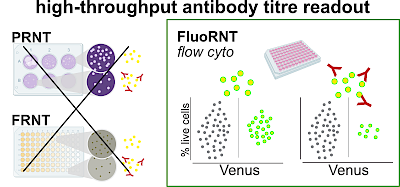
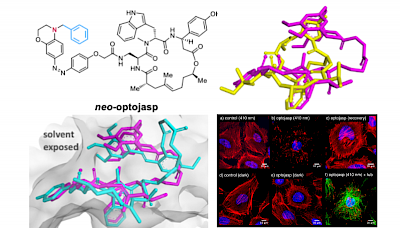
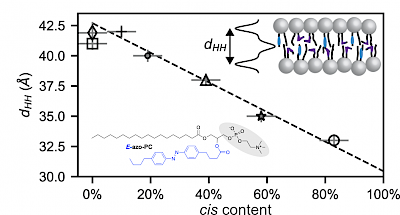
TS Group Publications
Oliver Thorn-Seshold's chemical biology group moved to TU Dresden in 2024.
Julia Thorn-Seshold's redox biology group moved to UKDD in 2025.
This webpage is no longer maintained.
|
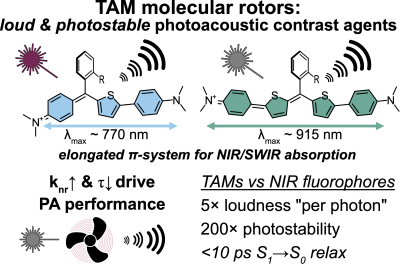
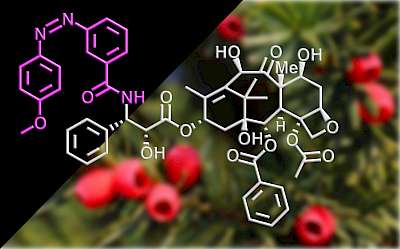
53* M Müller*, A Valavalkar, V Gujrati, JP Prohaska, D Shelar, M Kaltenegger, B Dietzek-Ivanšić, V Ntziachristos, O Thorn-Seshold*; Molecular rotors are loud, highly photostable, NIR/SWIR- active molecular optoacoustic contrast agents Photoacoustic imaging agents so far occupy a limited chemical space; and usually they are built by first choosing high-ε NIR-absorbing basis structures (developed for fluorophores) then later dialling down their fluorescence. We argue for a different conceptual approach to PA. We argue that since nonradiative decay rates control the intrinsic parameters that are most important for PA performance (paper 49), this usual design strategy must be rewritten: first choose a scaffold to deliver ultrafast decay, and only later tune ε & λmax. Here we introduce the first NIR/SWIR triarylmethane PA agents (a non-fluorophore chemical space), showing how molecular rotors can unlock quantitative longitudinal PA: a rational, mechanism-based design to improve dye performance in PA and a range of other basic and translational imaging methods. |
|
|
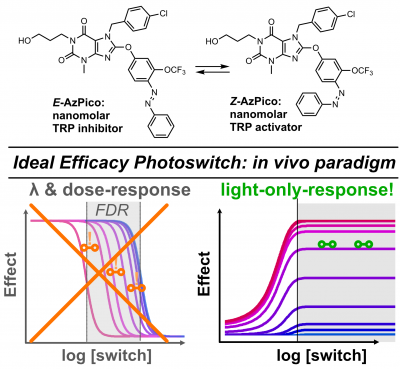
52* M Müller, K Niemeyer, NK Ojha, SA Porav, D Vinayagam, N Urban, F Büchau, K Oleinikov, M Makke, CC Bauer, AV Johnson, SP Muench, F Zufall, D Bruns, Y Schwarz, S Raunser, T Leinders-Zufall, RS Bon, M Schaefer*, O Thorn-Seshold*; Ideal efficacy photoswitches for TRPC4/5 channels harness high potency for spatiotemporally-resolved control of TRPC function in live tissues Here we identify and solve a previously-unrealised systematic problem that had blocked nearly all photoswitchable reagents from in vivo utility. To date, nearly all reagent designs were affinity photoswitches. These are easy to create by classic drug design, but since they intensiometric modulators, they are only effective when drug concentrations are fixed. This is fine for publishing results in 2D cell culture, but upon transition to in vivo work, ADME-PK makes them useless. This had left photopharmacology unable to compete with optogenetics, whose in vivo applicability is its greatest strength. |
|
|
51* O Thorn-Seshold*, V Glembockyte, B Baumgartner, A Wiegand; Stabilised Fluorophores, compositions, methods of preparation, conjugates thereof, and methods of use Under high-intensity imaging, even fluorophores with low intersystem crossing yields will enter triplet states. These "dark" (non-signal-generating), long-lived, and chemically reactive triplets are the primary cause of both fluorophore photobleaching and biological photodamage. Here we disclose a general method to depopulate triplets on the fly, to convert known fluorophores into high-brightness, long-lived, photoresistant and biologically innocent imaging agents. |
|
|
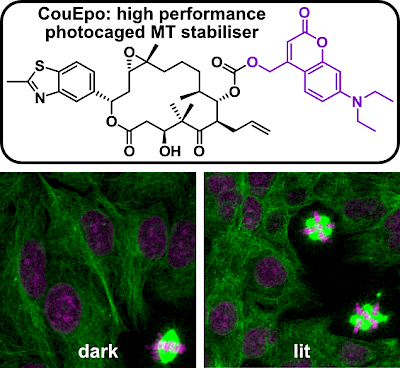
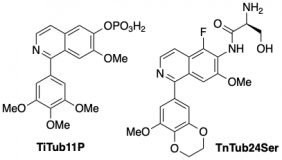
50* C Schmitt, P Mauker, N Vepřek, C Gierse, JCM Meiring, J Kuch, A Akhmanova, L Dehmelt, O Thorn-Seshold*; A Photocaged Microtubule-Stabilising Epothilone allows Spatiotemporal Control of Cytoskeletal Dynamics. Cytoskeleton research requires high-precision tools to locally manipulate the dynamics and organisation of cytoskeletal proteins. Yet, to date, no photoresponsive tool could unite the features needed for a practical, high-precision microtubule-stabilising reagent: i.e., (1) inactive when not lit; (2) efficient and clean photoconversion to a high potency drug; (3) good solubility at the working concentration; (4) efficient synthetic access. We present CouEpo, the first photocaged epothilone, which is a high-performance tool compound for photocontrolling microtubule dynamics in live cells on the micron scale. It can now support high-precision research into many microtubule-associated processes, from biophysics to transport, cell motility, and neuronal physiology. |
|
|
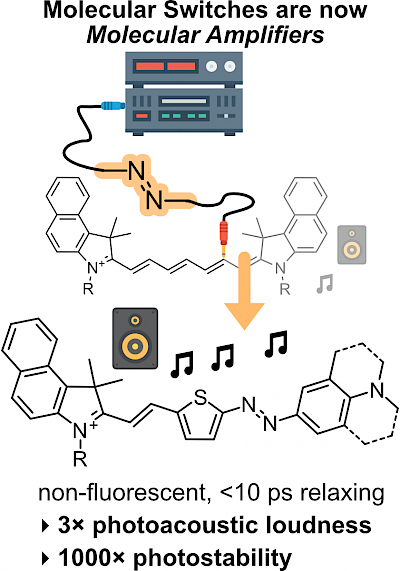
49* M Müller, N Liu, V Gujrati, A Valavalkar, S Hartmann, A Telek, B Dietzek-Ivanšić, A Hartschuh, V Ntziachristos, O Thorn-Seshold*; Merged molecular switches excel as optoacoustic dyes: azobenzene-cyanines are loud and photostable NIR imaging agents. Optoacoustic or Photoacoustic imaging can offer µm-resolution noninvasive imaging in biology, much deeper (>cm) than fluorescence. However, current NIR-absorbing small molecule contrast agents are not loud and photostable enough: most are simply repurposed fluorophores, with photoinstability or phototoxicity problems in optoacoustic imaging due to their slow S1→S0 relaxation. |
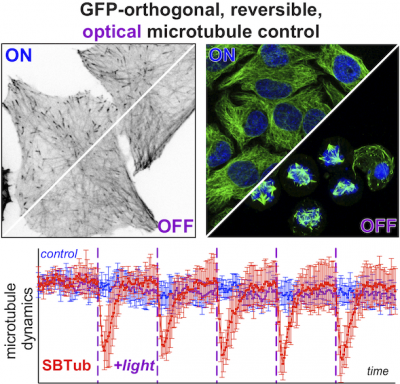
|
|
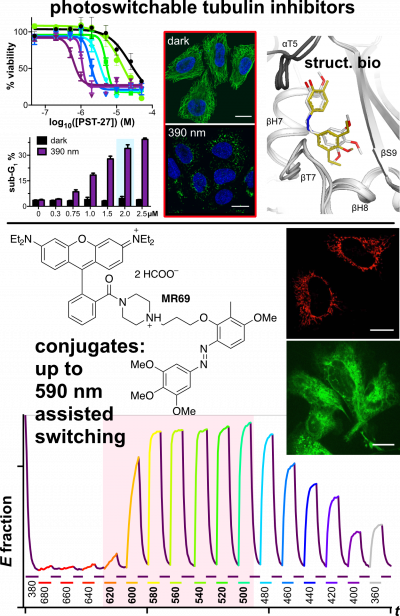
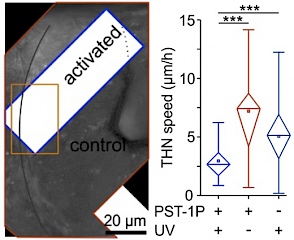
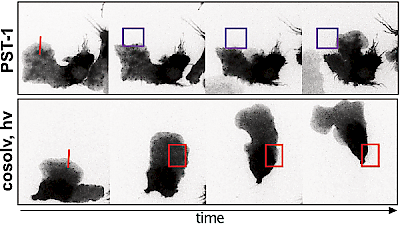
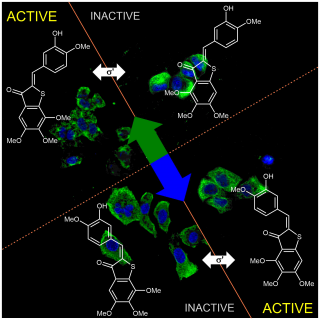
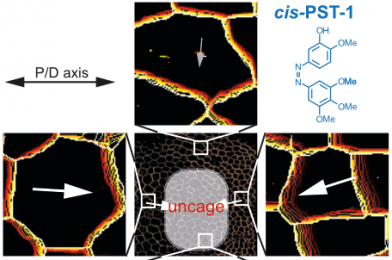
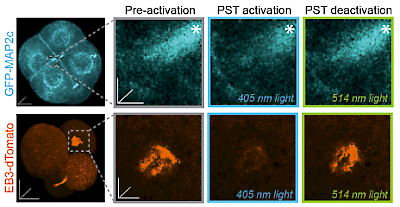
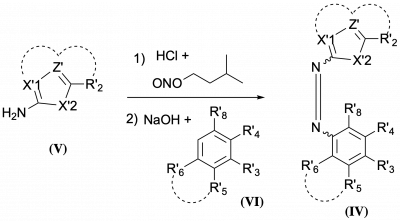
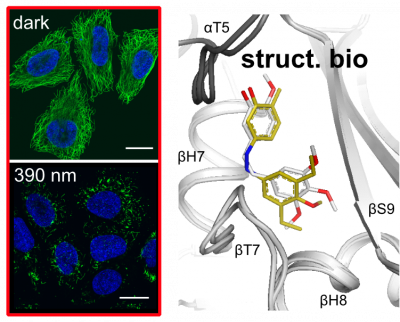
48* M Reynders, M Garścia, A Müller-Deku, M Wranik, K Krauskopf, L de la Osa de la Rosa, K Schaffer, A Jötten, A Rode, V Stierle, Y Kraus, B Baumgartner, A Ali, A Bubeneck, T Seal, MO Steinmetz, P Paulitschke, O Thorn-Seshold*; A photo-SAR study of photoswitchable azobenzene tubulin-inhibiting antimitotics identifying a general method for near-quantitative photocontrol. Photoswitchable combretastatin A4 azologues (photostatins, "PSTs") were previously developed to optically control microtubule dynamics in living systems. Now, (1) we used large-field-of-view, long-term photoswitching/microscopy to fill the gap between their seconds- and hours-scale photopharmaceutical bioactivity; and (2) we tested a panel of PST structural variations for photo-SAR to tune photoresponse and bioactivity, for GFP/YFP-compatible analogues. These results guide new design and applications for photoswitchable microtubule inhibitors. (3) We also attached fluorescent reporter "antennas", which greatly enhanced the long-wavelength single-photon photoisomerisation of azobenzenes by a hitherto un-explored mechanism (see e.g. papers 42 & 47), which will drive general progress towards near-quantitative long-wavelength photoswitching of photopharmaceuticals in biology. |
|
|
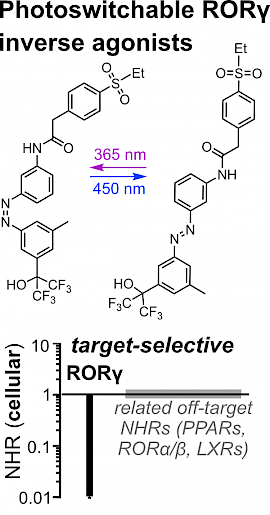
47* M Reynders*, S Willems, J Marschner, T Wein, D Merk*, O Thorn-Seshold*; A High-Quality Photoswitchable Probe that Selectively and Potently Regulates the Transcription Factor RORγ. Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor γ (RORγ) is a circadian regulator with a cyclic temporal role, as well as a spatially-localised target for experimental therapeutics in inflammation and immunity. To make tools to study RORγ biology with the spatial and temporal precision its biology requires, we designed photoswitchable RORγ inverse agonists that are a rare example of high-quality photoswitchable probes: combining nanomolar potency that can be photoswitched by >10-fold in cells, with outstanding selectivity over related nuclear receptors. These photopharmaceuticals can now serve as high-precision tools to study the dynamic modulation of RORγ in signaling pathways and in inflammatory disorders. |
|
|
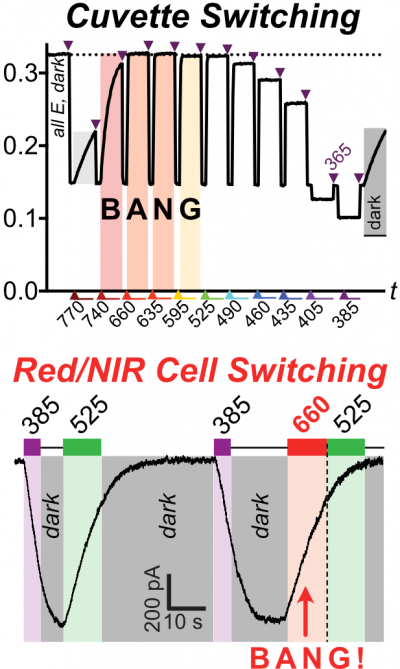
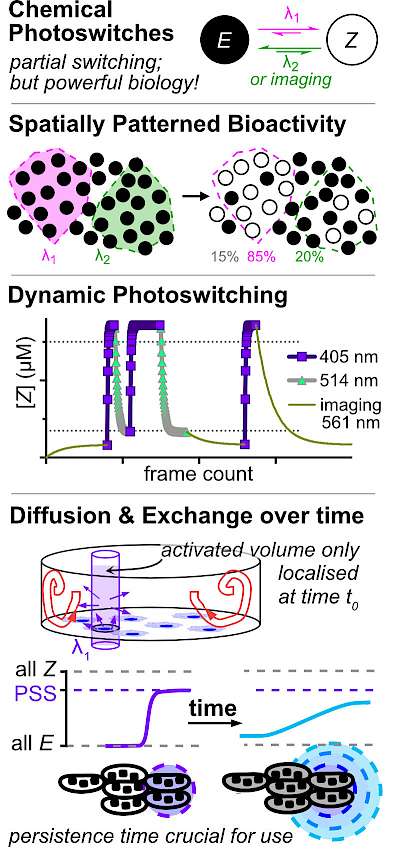
46* B Baumgartner, V Glembockyte, A Gonzalez-Hernandez, A Valavalkar, R Mayer, L Fillbrook, A Müller-Deku, J Zhang, F Steiner, A Wiegand, C Gross, M Reynders, H Munguba, A Arefin, A Ofial, J Beves, T Lohmüller, B Dietzek-Ivansic, J Broichhagen, P Tinnefeld, J Levitz, O Thorn-Seshold*; A General Method for Near-Infrared Photoswitching in Biology, Demonstrated by the >700 nm Photocontrol of GPCR Activity in Brain Slices. Azobenzene molecular switches are widely used to photocontrol cellular activity and material properties by E⇆Z photoswitching. However, since this photoswitching is incomplete, their dynamic range of property control is often small; and as they cannot be operated with red/NIR light, they are usually not applicable in deep tissue in vivo. Here, we pioneer a very general method for efficient single-photon >700 nm photocontrol of azobenzenes: conditional energy transfer from red/NIR chromophore auxiliaries to bioactive azobenzenes, driving bulk Z→E isomerisation to even >95% completeness with photon-efficiency that can be even higher than for direct azobenzene E→Z isomerisation in the UV region. The transfer reagents are biocompatible and photostable, and crucially, their performance properties are intrinsic: i.e. will perform identically at any dilution, and not be affected by biodistribution. We show that these dyads can be created straightforwardly from most azobenzenes, with most auxiliary chromophores, without tricky re-design or re-optimisation. After outlining some rules of auxiliary-based photoswitching, which can guide its broader adoption, we conclude by validating the method for single-far-red-photon photocontrol of glutamate receptor activity in live acute brain slices. (See also papers 45 & 48). |
|
|
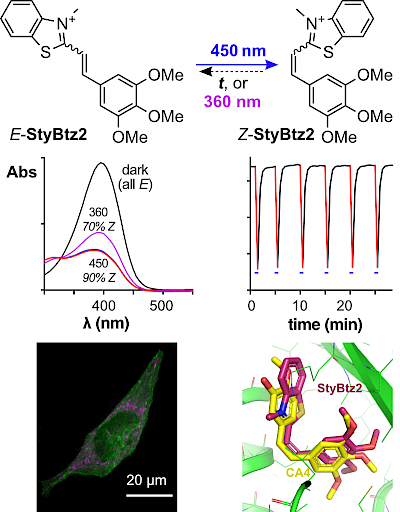
45* B Baumgartner, V Glembockyte, RJ Mayer, AJ Gonzalez-Hernandez, RO Kindler, A Valavalkar, AJ Wiegand, A Müller-Deku, L Grubert, F Steiner, C Gross, M Reynders, V Grenier, J Broichhagen, S Hecht, P Tinnefeld, AR Ofial, B Dietzek-Ivanšic, J Levitz, Azobenzenes can achieve near-infrared photocontrol in biological systems, with quantitative Z→E photoisomerization, via singlet manifold photoredox. Despite two decades of optogenetics and photopharmacology, we still cannot photoswitch bioactivity with NIR light: so we are blocked from true in vivo applications of these powerful and diverse reagents. |
|
|
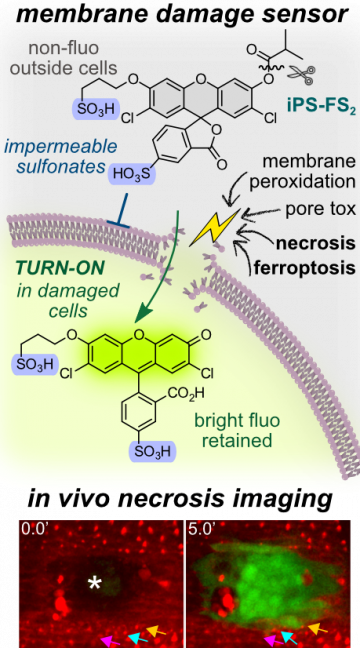
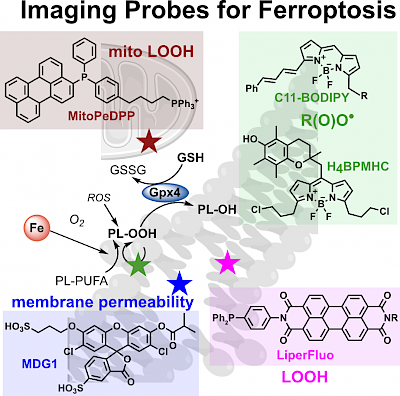
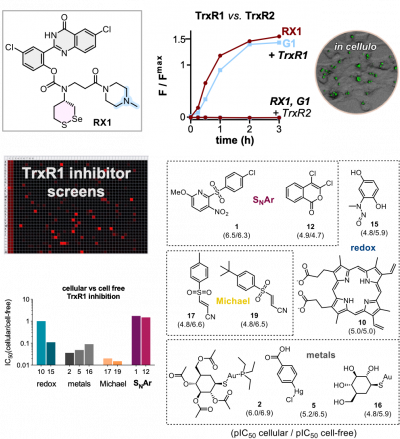
44* P Mauker, D Beckmann, A Kitowski, C Heise, C Wientjens, AJ Davidson, S Wanderoy, G Fabre, A Harbauer, W Wood, C Wilhelm, J Thorn-Seshold, T Misgeld, M Kerschensteiner, O Thorn-Seshold*; Fluorogenic chemical probes for wash-free imaging of cell membrane damage in ferroptosis, necrosis, and axon injury. Selectively labelling cells with damaged membranes is needed in contexts as simple as identifying dead cells in culture, or as complex as imaging membrane barrier functionality in vivo during ferroptosis or necrosis. To do this more powerfully, we require tools that no longer need removal of extracellular signal before imaging. |
|
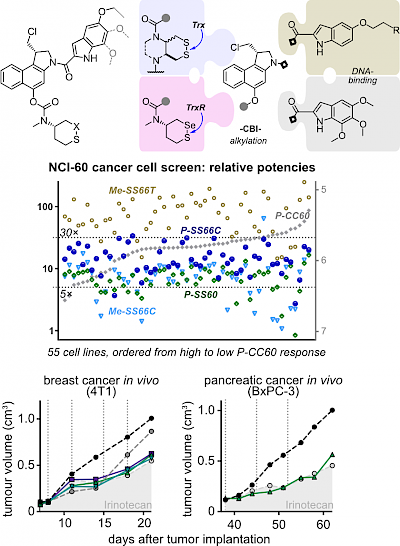
|
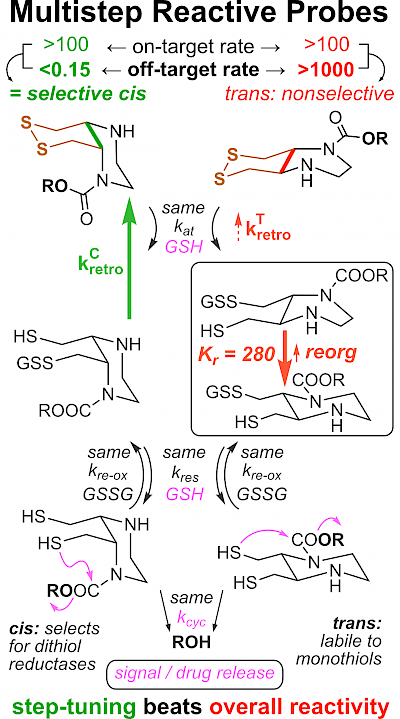
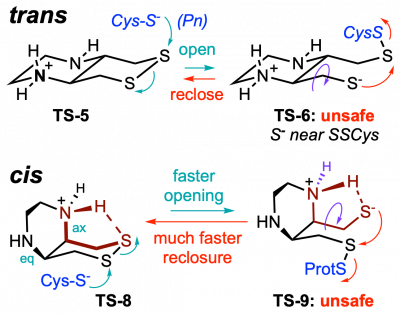
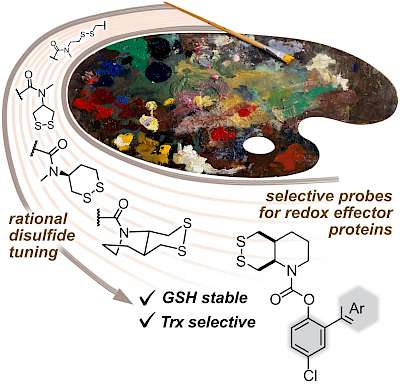
43* L Zeisel#, J Felber#, K Scholzen, C Schmitt, A Wiegand, L Komissarov, E Arnér, O Thorn-Seshold*; Piperazine-fused cyclic disulfides: high-performance bioreduction-activated cores for bifunctional probes and reagents. "Concept summary": The classic limitation of single-step reactive probes is that increasing reactivity comes at the cost of decreased selectivity. We now show that multi-step cascades can tune selectivity and reactivity independently: so, when the rate-limiting steps are different between on-target and off-target pathways, chemical design addressing these steps separately can increase both selectivity and reactivity, to access unprecedently powerful probes for biological systems. "User summary": there were no cellularly-effective reagents to selectively address dithiol reductases like Trxs and Grxs. We developed piperazine-fused six-membered-cyclic disulfides to fill this gap. These probes are >100-fold faster redox-activated than any previously known; are good substrates for thioredoxins; and can selectively and effectively report Trx activity in live cells. Late-stage diversifications can apply these motifs not just in redox probes and prodrugs, but also for solid phase synthesis or antibody-drug conjugates. This work thus establishes tuned dichalcogenides as flexible and effective bioreductive triggers for cellular redox biology. |
|
|
42* O Thorn-Seshold*, J Felber*, L Zeisel*; Cyclic Dichalcogenide ADC Linker Units and Uses Thereof. A modular drug delivery system using intracellular dichalcogenide redox. |
 |
|
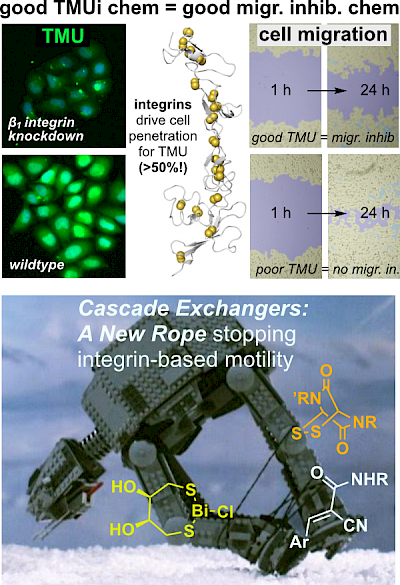
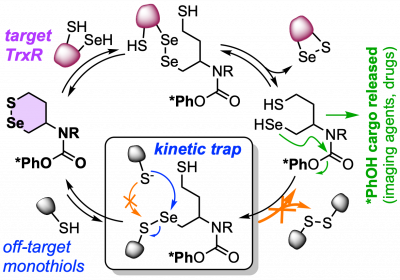
41* F Coelho, L Zeisel, O Thorn-Seshold*, S Matile*; Selenium-Centered Cascade Exchangers and Conformational Control Unlock Unique Patterns of Thiol-Mediated Cellular Uptake Introducing cyclic selenenylsulfides (SeS) as a new dynamic-covalent electrophile motif that can reversibly engage cell-surface thiols to increase thiol-mediated cargo uptake (TMU) into cells. We show how remote ammoniums and conformational effects can tune uptake activity, and show that SeS are unique in that they actually increase the TMU of co-applied Michael acceptors. This also underscores the complex links between exofacial redox status, and real or apparent intracellular redox activity. |
|
|
40 C Berndt*; coauthors incl. C Schmitt, O Thorn-Seshold, & 88 more; M Conrad*; Ferroptosis in health and disease §6.3.1: Fluorescent Probes to Investigate Ferroptosis Ferroptosis is a non-apoptotic mode of cell death where phospholipid hydroperoxides are formed by peroxidation chain reactions, leading to plasma membrane rupture. How lipid peroxidation is initiated or prevented, and how it causes ferroptosis, are subjects of intense research; but investigating these requires solid biochemical techniques to quantify and speciate the molecular actors involved. Our section in this mega-review is a short critical review of the fluorescent probes for tracking and characterising ferroptosis-related cellular features. |
|
|
39* J Felber, A Kitowski, L Zeisel, M Maier, C Heise, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Cyclic dichalcogenides extend the reach of bioreductive prodrugs to harness the thioredoxin system: applications to seco-duocarmycins. Despite their crucial roles in physiology as well as links to cancer and inflammation, cellular dithiol-type oxidoreductases such as Trx/TrxR cannot be addressed by current bioreductive prodrugs, that mainly cluster around oxidised nitrogen species. |
|
|
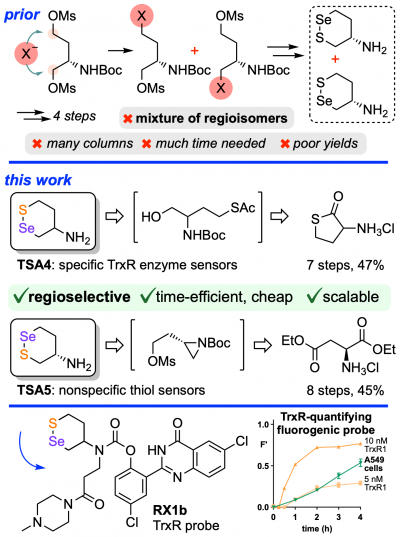
38* L Zeisel*, M Maier, O Thorn-Seshold*; Regioselective, efficient and scalable syntheses of 1,2-thiaselenanes. 1,2-thiaselenane-amines are valuable redox-active motifs for chemical biology, but their use is hindered by tedious synthesis. |
|
|
37 F Coelho, S Saidjalolov, D Moreau, O Thorn-Seshold, S Matile*; |
|
|
36 M Wranik*, M Kepa*, et al, K Krauskopf, L Gao, O Thorn-Seshold, C Bostedt, C Bacellar, M Steinmetz, C Milne, J Standfuss*; |
 |
|
35 C Velasco, R Santarella-Mellwig, M Schorb, L Gao, O Thorn-Seshold, A Llobet; |
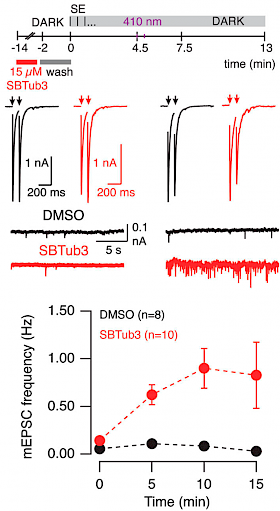 |
|
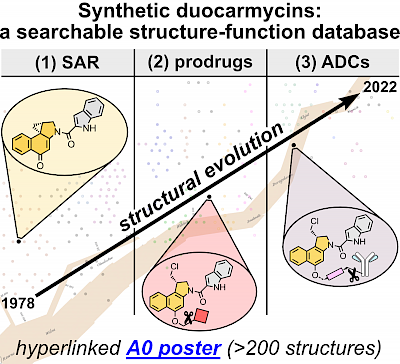
34* J Felber*, O Thorn-Seshold*; 40 Years of Duocarmycins: A Graphical Structure/Function Review of Their Chemical Evolution, from SAR to Prodrugs and ADCs. Duocarmycins are picomolar cytotoxins with fascinating, cyclisation-based bioactivity. |
|
|
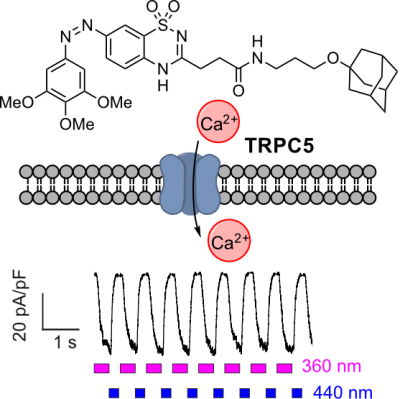
33* M Müller, K Niemeyer, N Urban, N Ojha, F Zufall, T Leinders-Zufall, M Schaefer, O Thorn-Seshold*; BTDAzo - a photoswitchable TRPC5 channel activator. The TRPC5 calcium-permeable cation channel has distinct tissue-specific roles, from synaptic function to hormone regulation. |
|
|
32* L Zeisel, J Felber, K Scholzen, L Poczka, D Cheff, M Maier, Q Cheng, M Shen, M Hall, E Arnér, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Selective cellular probes for mammalian thioredoxin reductase TrxR1: rational design of RX1, a modular 1,2-thiaselenane redox probe. The answer is Selenium! The question: how to make small molecule probes that are selective cellular reporters of the unique selenol/thiol redox enzyme Thioredoxin Reductase (TrxR), an upstream driver in metabolism and disease? Lukas' Potential Energy highlight: 10.1016/j.chempr.2022.04.014 (gp4s84) |
|
|
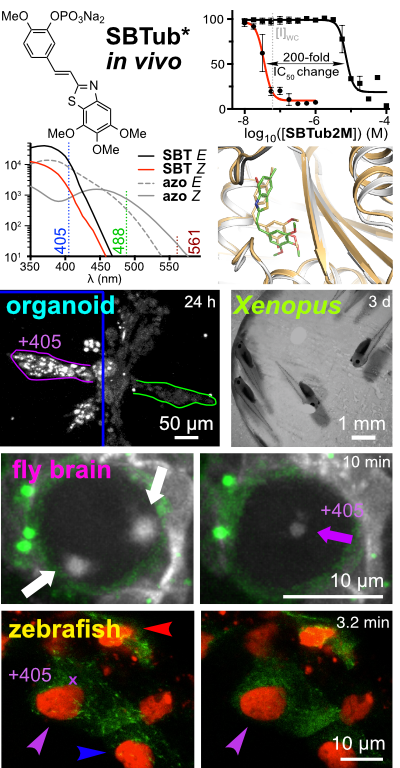
31* L Gao, J Meiring, A Varady, I Ruider, C Heise, M Wranik, C Velasco, J Taylor, B Terni, J Standfuss, C Cabernard, A Llobet, M Steinmetz, A Bausch, M Distel, J Thorn-Seshold, A Akhmanova, O Thorn-Seshold*; In vivo photocontrol of microtubule dynamics and integrity, migration and mitosis, by the potent GFP-imaging-compatible photoswitchable reagents SBTubA4P and SBTub2M. Photopharmaceuticals in 2D cell culture can deliver target-selective potency with spatiotemporal specificity, through local illumination of globally-treated samples. But in 3D and in vivo, this has essentially not been reproduced. |
|
|
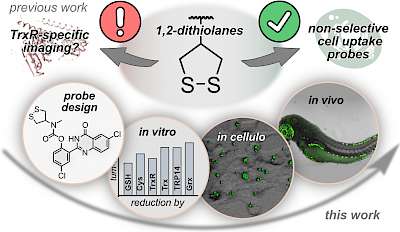
30* J Felber, L Poczka, K Scholzen, L Zeisel, M Maier, S Busker, U Theisen, C Brandstädter, K Becker, E Arnér, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Cyclic 5-membered disulfides are not selective substrates of thioredoxin reductase, but are opened nonspecifically by thiols. Cyclic five-membered disulfides (S50 dithiolanes) are kinetically labile motifs, that are widely used as "TRFS" redox probes for thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) e.g. in inhibitor screening and disease analysis. |
|
|
29* L Gao, Y Kraus, A Stegner, T Wein, C Heise, L von Brunn, E Fajardo-Ruiz, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Self-reporting styrylthiazolium photopharmaceuticals: mitochondrial localisation as well as SAR drive biological activity. Novel photoswitches are needed to drive advances in photopharmacology. |
|
|
28* A Müller-Deku, O Thorn-Seshold*; Exhaustive catalytic ortho-alkoxylation of azobenzenes: flexible access to functionally diverse yellow-light-responsive photoswitches. Per-ortho-alkoxylated azobenzenes have attractive photoswitching and functional potential, but were a nightmare to synthesise systematically. |
|
|
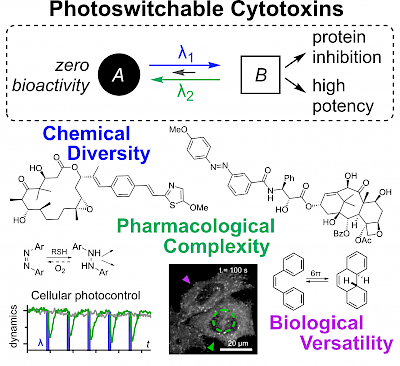
27* O Thorn-Seshold*; Chapter 36: Photoswitchable Cytotoxins (pp 873-919) Cytotoxins are drugs whose targets are so essential to biology that inhibiting them causes cell death. Photoswitchable analogues of these cytotoxins promise valuable applications, leveraging high-precision optical control for unique modulation studies of these essential biological targets. However, they face stricter challenges in design and validation than other classes of photopharmaceuticals. Developments in the last decade have targeted the cytoskeleton, structural and genomic integrity, and signaling; and principles for the creation and use of these reagents have been clarified. The stage is set for further applications of photoswitchable cytotoxins in the life sciences. |
|
|
26* O Thorn-Seshold*, J Meiring; Chapter 26: Photocontrolling Microtubule Dynamics with Photoswitchable Chemical Reagents (pp 403-430) A practical quick-start guide for biologists to use photoswitchable chemical reagents in cells. Optically controlling microtubules in vivo has gone from dream to reality in less than a decade. A range of photoswitchable chemical MT inhibitors from our group now allow sub-second and micron-scale spatiotemporal resolution of inhibition over MT dynamics and MT-dependent processes. However, there were still no user guides for biologists to establish photopharmaceutical assays; and the principles for high-quality assay design and validation have not been codified even in the chemistry community. We present: (i) the basics of photoswitching small molecules; These methods are generally translatable to establishing and benchmarking assays with photopharmaceuticals for any protein target; and should help chemists to develop photoswitchable reagents more robustly, as well as equipping biologists to apply them further to 3D culture and in vivo. |
|
|
25. J Rushworth, et al., O Thorn-Seshold, M Fuchter*; |
|
|
24. M Scheck, et al., G Barba-Spaeth, O Thorn-Seshold, A Krug, S Endres, S Rothenfusser*, J Thorn-Seshold*; |
|
|
23. F Küllmer, N Vepřek, et al., O Thorn-Seshold, H-D Arndt, D Trauner; |
|
|
22. M Ober, A Müller-Deku, et al., O Thorn-Seshold, B Nickel; |
|
|
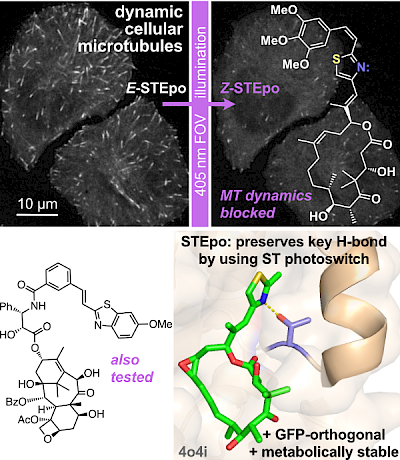
21* L Gao, J Meiring, C Heise, A Rai, A Müller-Deku, A Akhmanova, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Photoswitchable epothilone-based microtubule stabilisers allow GFP-imaging-compatible, optical control over the microtubule cytoskeleton. Epothilone and Taxol, C=C photoswitches new and old: here, we bring the GFP-orthogonal azobenzene isostere styrylthiazole (ST) into photopharmacology. The nanomolar-potent STEpo reagents are photoswitchably microtubule-stabilising reagents with micron-precise targeting and intriguing potential towards in vivo applications. |
|
|
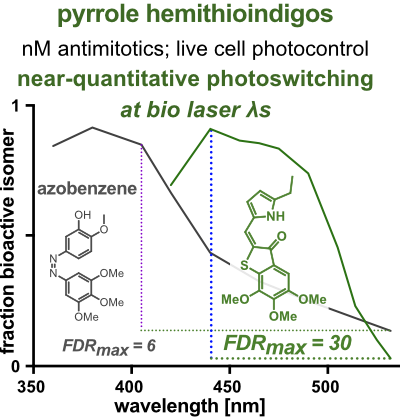
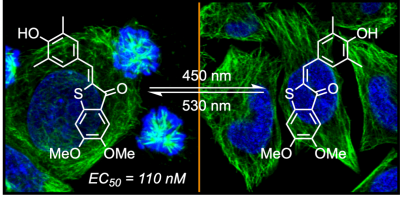
20* A Sailer, J Meiring, C Heise, L Pettersson, A Akhmanova, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Pyrrole hemithioindigo antimitotics with near-quantitative bidirectional photoswitching photocontrol cellular microtubule dynamics with single-cell precision. Most photopharmaceuticals suffer background activity, as their photoswitching is incomplete. Our PHTubs are near-quantitatively-switchable reagents that deliver cell-precise real-time photocontrol over microtubule dynamics, cell cycle, and cell death, for high-precision cytoskeleton research. This is the first use of hemithioindigos for high-resolution control in live cell assays, and shows PHTs may be excellent scaffolds for a range of other biological targets. |
|
|
19* J Felber, L Zeisel, L Poczka, K Scholzen, S Busker, M Maier, U Theisen, C Brandstädter, K Becker, E Arnér, J Thorn-Seshold, O Thorn-Seshold*; Selective, modular probes for thioredoxins enabled by rational tuning of a unique disulfide structure motif. Cyclic disulfides have a lot of potential for redox biology! Here we rationally design unique S6x disulfides, invoking a combination of considerations for topology, thermodynamics, and kinetics. These give the only disulfide-based probes that can resist the cellular monothiol background; and they proved to be selectively triggered by the central redox effector protein, thioredoxin (Trx). The methodology in this paper forms the basis for our longterm project on redox biology. |
|
|
18* L Gao, J Meiring, Y Kraus, M Wranik, T Weinert, S Pritzl, R Bingham, E Ntouliou, K Jansen, N Olieric, J Standfüss, L Kapitein, T Lohmüller, J Ahlfeld, A Akhmanova, M Steinmetz, O Thorn-Seshold*; A robust, GFP-orthogonal photoswitchable inhibitor scaffold extends optical control over the microtubule cytoskeleton. It's no use photoswitching if you can't see what you're doing, or if the switch falls apart while you use it. These heterostilbene SBTubs were developed to leave GFP/YFP imaging channels free, and also resist in vivo metabolism. They allow exquisitely orthogonal photocontrol of cellular microtubule dynamics with minimal crosstalk/bleaching. |
|
|
17* O Thorn-Seshold*, J Felber, J Thorn-Seshold, L Zeisel; Disulfide prodrug compounds. A modular probe & prodrug system using disulfide redox chemistry. |
 |
|
16* O Thorn-Seshold*, L Zeisel, J Felber; Dichalcogenide Prodrugs. A modular probe & prodrug system using dichalcogenide redox chemistry. |
 |
|
15* A Müller-Deku, J Meiring, K Loy, Y Kraus, C Heise, R Bingham, K Jansen, X Qu, F Bartolini, L Kapitein, A Akhmanova, J Ahlfeld, D Trauner, O Thorn-Seshold*; Photoswitchable paclitaxel-based microtubule stabilisers allow optical control over the microtubule cytoskeleton. These AzTax reagents (azobenzene-extended taxols) are the first photoswitchable microtubule stabilisers. They enable cellularly- and subcellularly-specific photocontrol of MT polymerisation dynamics, incl. in primary neurons. |
|
|
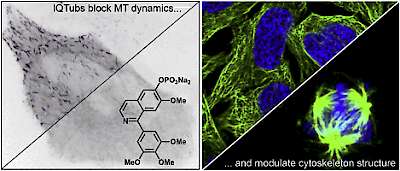
14* Y Kraus#, C Glas#, B Melzer, L Gao, C Heise, M Preuße, J Ahlfeld, F Bracher, O Thorn-Seshold*; Isoquinoline-based biaryls as a robust scaffold for microtubule inhibitors. Colchicinoids have two aryl blades separated by a bridge that is often metabolically or photochemically labile. These IQTub biaryls are highly robust; easy to make and diversify; and are potent druglike cellular binders. |
|
|
13* A Sailer, F Ermer, Y Kraus, R Bingham, F Lutter, J Ahlfeld, O Thorn-Seshold*; Potent hemithioindigo-based antimitotics photocontrol the microtubule cytoskeleton in cellulo. Improving on our first generation photoswitchable microtubule inhibitor HTIs, these HITubs are mid-nanomolar cell-active photoswitchable tubulin binders with all-visible-light switching, illustrating the potential of the HTI scaffold for cell biology. |
|
|
12. U Theisen, A Ernst, R Heyne, T Ring, O Thorn-Seshold, R Köster; |
|
|
11. M Borowiak, F Küllmer, F Gegenfurtner, S Peil, V Nasufovic, S Zahler, O Thorn-Seshold, D Trauner, H-D Arndt; |
|
|
10. A Kopf, J Renkawitz, R Hauschild, I Girkontaite, K Tedford, J Merrin, O Thorn-Seshold, D Trauner, H Häcker, K-D Fischer, E Kiermaier, M Sixt; |
|
|
9. M Bischof, S Olthoff, C Glas, O Thorn-Seshold, M Schaefer, K Hill; |
|
|
8* O Thorn-Seshold*; Comment on “Photo-Controlled Reversible Microtubule Assembly”. Metabolically labile inhibitor-photoswitch attachment strategies and PAINS-like aggregation modulation can confound reagent design. This critique to Liu et al., ACIE 2018 highlights the danger of neglecting controls and SAR. Despite their followup showing that non-inhibitors give identical effects as claimed inhibitors (Liu et al., ACIE 2019) the file remains open at ACIE: in the meantime, the papers were not retracted or corrected, and their citation net continues (author response here). |
|
|
7* A Sailer, F Ermer, Y Kraus, F Lutter, C Donau, M Bremerich, J Ahlfeld, O Thorn-Seshold*; Hemithioindigos for cellular photopharmacology: desymmetrised molecular switch scaffolds enabling design control over the isomer-dependency of potent antimitotic bioactivity. The understudied hemithioindigos have more attractive photoswitching than standard azobenzenes. These HOTubs are the first HTI-pharmacophore reagents to succeed in cell biology, and enable desymmetrised designs. |
|
|
6* O Thorn-Seshold*, F. Bracher, B. Melzer; Isoquinoline biaryl compounds. IQTubs are diversifiable, metabolically robust isosteres for cis-stilbenoid bioactives. |
|
|
5. A Singh, T Saha, I Begemann, A Ricker, H Nüsse, O Thorn-Seshold, J Klingauf, M Galic, M Matis; |
|
|
4. J Zenker, MD White, RM Templin, RG Parton, O Thorn-Seshold, S Bissiere, N Plachta; |
|
|
3. K Eguchi, Z Taoufiq, O Thorn-Seshold, et al., T Takahashi; |
|
|
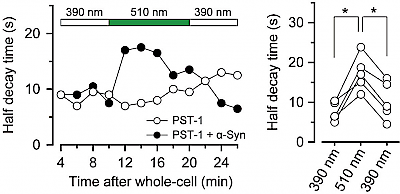
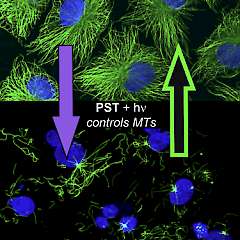
2* M Borowiak, et al., D Trauner*, O Thorn-Seshold*; Photoswitchable Inhibitors of Microtubule Dynamics Optically Control Mitosis and Cell Death. Reversible photoswitching of PSTs allows bidirectionally reversible optical modulation of MT dynamics in live cells, and modifies cell division sequences during embryonic development. |
|
|
1* O Thorn-Seshold*, M Borowiak, D Trauner, J Hasserodt; Azoaryls as Reversibly Modulatable Tubulin Inhibitors. Reversibly photoswitchable isosteres of stilbenoid colchicine-mimic drugs ("PSTs") for in vitro and in vivo control of microtubule dynamics. |