Photocontrolling Microtubules & Cell Migration, Division, Transport
Oliver Thorn-Seshold's chemical biology group moved to TU Dresden (link) in 2024.
Julia Thorn-Seshold's redox biology group moved to UKDD (link) in 2025.
This webpage is no longer maintained.
The cellular scaffolding protein tubulin is the monomeric unit that forms the complex, highly dynamic network of cellular microtubules - gigantic, noncovalent polymeric assemblies that act as roads for cellular trafficking, parking lots for resting proteins, and as girders for applying or sensing forces within (and outside of) cells. Microtubules are continuously being built up, torn down, modified with chemical flags (PTMs), and coordinated by a host of proteins into rapidly changing shapes. These remodelling dynamics are crucial to the correct functioning of many anisotropic cellular processes, most famously, to the separation of genetic material and daughter cells during mitosis/meieosis. Many of the most powerful anticancer drugs (taxanes, vinca alkaloids, discodermolides) work by altering these microtubule dynamics so that cells can no longer divide correctly and instead go into apoptosis.
Our research has pioneered photoisomerisable microtubule inhibitors, that can be precisely controlled through reversible optical patterning. These photopharmaceutical antimitotics are allowing researchers to use light to reversibly modulate microtubule-dependent processes in eukaryotes, in 2D and 3D cell culture, as well as in vivo across model organisms from worm and fly to fish, frog, and mouse: with applications in fields from cargo transport to cell migration, cell division, and embryonic development. These results were made possible by merging the right molecular photoswitches, several of which we have pioneered, with the appropriate drug cores: and taking the resulting photopharmaceuticals through cellular to early in vivo biological testing. We are now stretching the chemical space of antimitotics and photoswitches to reach new generations of photoswitchably bioactive drugs with improved potency, in vivo compatibility, and other layers of functionality including subcellular localisation and tissue-retention.
A biologist's guide to MT photocontrol: Thorn-Seshold & Meiring 2022 in Methods in Molecular Biology (Springer).
A chemist's guide to photoswitchable antimitotics: Thorn-Seshold 2022 in Molecular Photoswitches (Wiley).
Swiss National Radio's popular science view on photopharmacology informing drug design (@18:15; OTS @ 25:00).
For our full list of papers on MT reagent development and applications, see the Publications page.
Primary research highlights include:
 |
 |
 |
 |
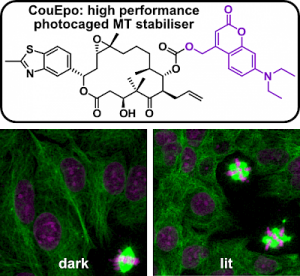
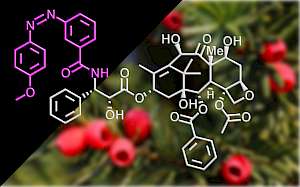
| Photocaged epothilone stabiliser CouEpo (Angewandte 2024) |
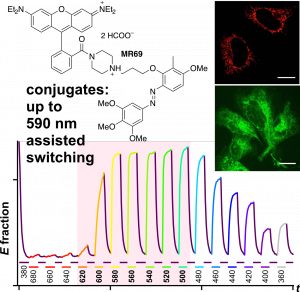
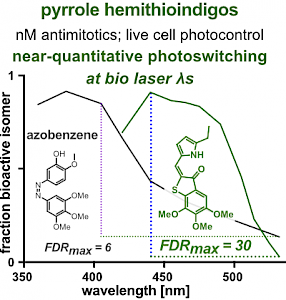
PST27 & MR69: Photo-SAR of MT photoswitches (Chem Sci 2024) |
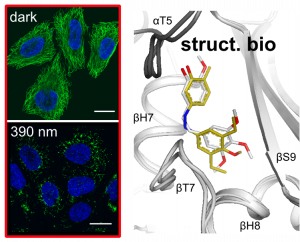
Struct. biol. of low-occupancy MT switches (Nat Comm 2023) |
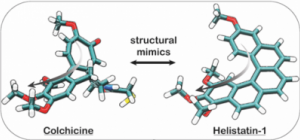
Helistatin: the first bioactive helicene (JACS Au 2022) |
|
|
|
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
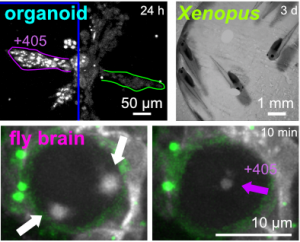
| Optimised SBTubs: in vivo MT photocontrol (JACS 2022) |
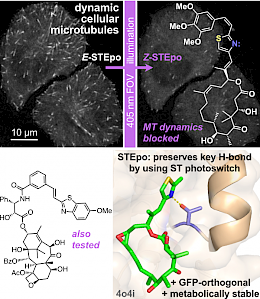
STEpo: epothilone MT photoswitch stabilisers (Angewandte VIP 2022) |
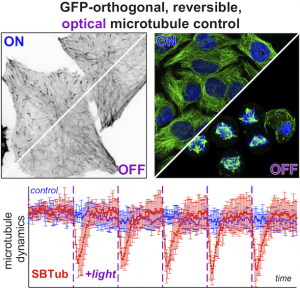
SBTub: GFP-orthogonal MT photoswitches (Cell Chem Biol 2021) |
PHTub: Laser-adapted MT photocontrol reagents (Angewandte 2021b) |
|
|
|
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
| AzTax: taxol-based MT photoswitch stabilisers (Nat Commun 2020) |
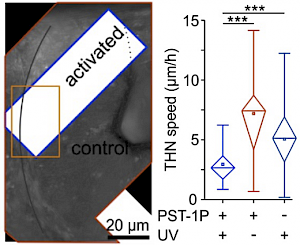
MT photocontrol in cell migration (J Cell Biol 2020b) |
HITub: high-potency HTI-based MT inhibitors (Beilstein JOC 2020) |
MT photocontrol in neurogenesis (J Cell Biol 2020a) |
|
|
|
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
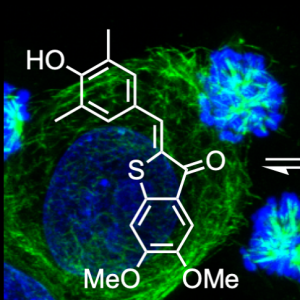
| HOTub: HTI-based photoswitches for MTs (ChemBioChem 2019) |
MT photocontrol in fly tissue morphogenesis (Nat Cell Biol 2018) |
MT photocontrol in mouse embryo development (Science 2017) |
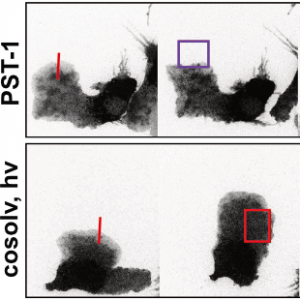
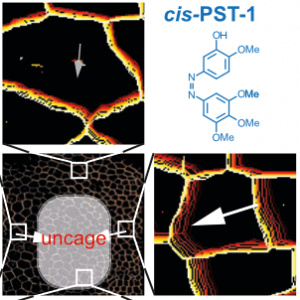
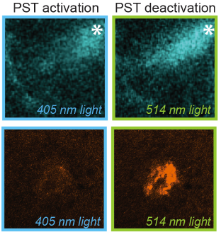
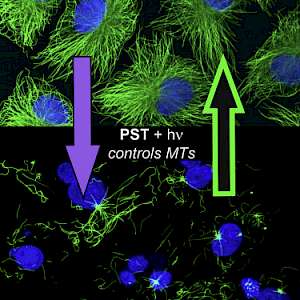
PST: azobenzene-based photoswitches for MTs (Cell 2015) |
The starting-point for this research axis was our development of photoswitchable microtubule inhibitors based around azobenzenes, for the colchicine binding site on tubulin, called PSTs. UV/blue or green illuminations switch PSTs between the inactive E isomer and the MT-inhibiting Z isomer, so they could light-specifically interrupt MT-dependent processes in cells and organisms, from mitosis to embryonic development. This cell-by-cell, reversible control had never previously been possible without genetic engineering. PSTs have since been distributed to >200 research groups for a range of cytoskeleton studies; while we have built up a reagent toolchest of photoresponsive MT inhibitors with better usability: such as compatibility with GFP/YFP for multichannel imaging studies; metabolic stability for long-term use in small animals; either rapid or slow switch-off for studies on different timescales; enhanced potency and solubility for organoid and in vivo experiments; rapid isomerisation for time-resolved structural biology; and subcellularly-precise targeting in cells. Our technical advances in these areas can also be applied to photocontrol of other protein systems, which is helping to expand the scope and applications of photopharmacology in general. In parallel though, we and others have explored the biological applications of our photoswitchable MT inhibitors as reagents to study force generation, cell migration, organoid growth, tissue morphogenesis, and embryonic development, across a range of model systems and organisms, aiming to shed more light on the many roles of MT dynamics and network structure in biology.


